
Can Scrunch show what sources are being cited by AI models in their responses?
- Also asked as:
- Does Scrunch show AI citation sources?
- Can I see which websites AI models reference?
Yes, Scrunch shows exactly which sources are being cited by AI models, including branded, competitive, and third-party sources, as part of its Citations feature.
Additional context: Every time an AI model (such as ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, etc.) responds to a prompt a user is tracking, Scrunch records which webpages were referenced.
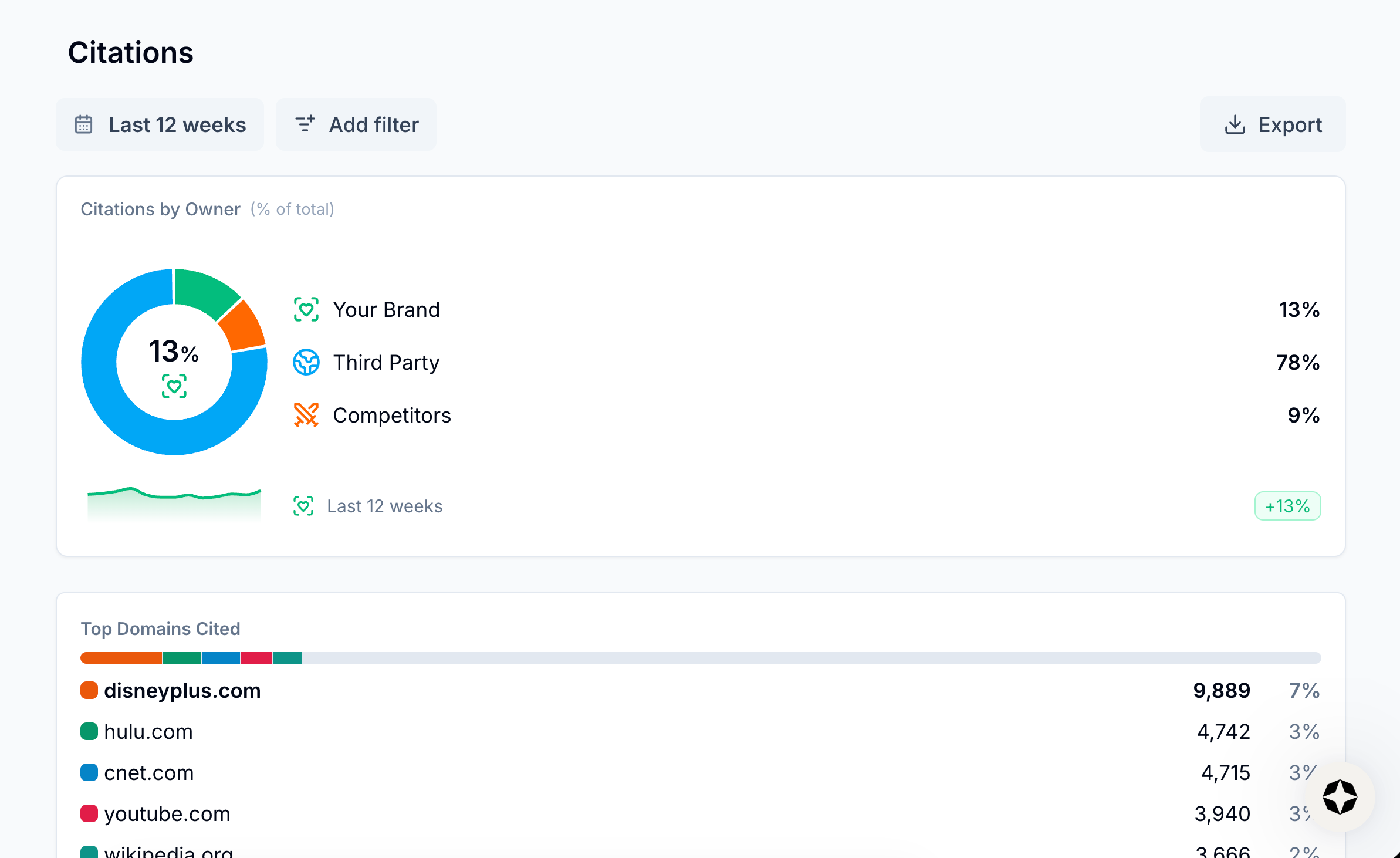
Example
For example, imagine a Scrunch user wants to understand which sources are being cited by LLMs for the prompts that they’re tracking.
In Scrunch’s Citations tab, they can view citation share broken down by owner (their brand, competitors, and third parties) and top cited domains.
For each source (filterable by website domain or webpage URL), they can see:
- Brand or competitor mentions
- Brand-relevant topic coverage
- Unique prompt count
- Total citations
- Citation consistency rate
- Influence Score (calculated by multiplying the unique number of prompts by the percentage of responses that have cited the source)
All citation data can be filtered by:
- Timeframe
- Branded vs. non-branded prompts
- Custom prompt tags
- Persona
- Country
- Prompt topic
- Citation topic
- AI platform
- Funnel stage
- Citation owner
Follow-up question: What counts as a citation in Scrunch?
Scrunch defines a citation as any URL that was cited by an AI platform when answering a tracked prompt. Each time Scrunch collects an AI response, it scans for the full list of URLs cited, which pages contributed to the AI response, whether a user’s (or competitor’s) brand appears on those pages, and which topics the page content relates to (based on a user’s Key Topics).
If brand isn’t shown as present when mentioned in cited source: JavaScript-only content, bot-blocking, and temporary retrieval errors may prevent Scrunch from accessing full page content from citation sources.
Related FAQs
What methods does Scrunch use to collect data from AI platforms?
Scrunch uses multiple methodologies to collect prompt data from AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and others, including browser automation and official platform APIs.
How do I create and use customer personas in Scrunch?
Scrunch allows users to create customer personas based on unique characteristics and geographies and either auto-generate prompts based on those personas or assign personas to existing prompts for targeted tracking and filtering.
Which AI platforms and LLMs can Scrunch track and monitor?
Scrunch currently supports seven major AI platforms: ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity, Google AI Mode, Google AI Overviews, and Meta AI. Support for Microsoft Copilot and Grok is coming soon.